CAPTCHA Bots: What They Are, How They Work, and How to Stop Them
18 Jun 2024 • 10 min read
CAPTCHA Bots: What They Are, How They Work, and How to Stop Them
18 Jun 2024 • 10 min read
Websites are under constant pressure to defend against malicious automation today. One of the most common defenses is the CAPTCHA (short for “Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart”), which was designed to block bots from filling out forms, creating accounts, or scraping content by introducing small but significant challenges that humans can easily solve.
But cybersecurity is a constant cat-and-mouse game. In response to CAPTCHA systems, attackers have created CAPTCHA bots—automated programs that solve CAPTCHAs and slip past protections to abuse systems for profit. From fake accounts to scraping and fraud, these bots are becoming a serious risk to businesses, users, and digital platforms worldwide.
This article will break down what CAPTCHA bots are, how they work, what risks they pose, and what you can do to defend your business.
What Are CAPTCHA Bots?
CAPTCHA bots are automated programs specifically built to solve or bypass CAPTCHA challenges, giving unauthorized access to systems designed to be human-only. Unlike traditional bots that perform basic tasks like scraping or crawling, CAPTCHA bots are more refined—they're often integrated into larger attack chains and used for high-value targets.
The CAPTCHA bots are commonly used in:
- Mass account creation for spreading spam, misinformation, or running fraud schemes
- Brute-force login attempts, especially when paired with leaked password lists (credential stuffing)
- Data scraping where CAPTCHA is used as a protective layer over valuable data or pricing models
- Bypassing ticketing or purchasing limits, hoarding inventory to resell at inflated prices
- Automated abuse of promotional offers, loyalty programs, or signup-based discounts
Cybercriminals leverage these bots not just for speed and scale but for profit. CAPTCHA bypassing becomes especially lucrative in industries like e-commerce, fintech, social media, and event ticketing. In some cases, CAPTCHA bots are rented out as a service or embedded into larger malware toolkits.
How CAPTCHA Bots Work

The architecture of CAPTCHA bots can range from simple scripts to full-blown AI-driven systems. Their success depends on how well they mimic human behavior and evade detection mechanisms. Here are the primary methods used:
1. OCR (Optical Character Recognition)
Traditional CAPTCHAs relied on distorted text or characters. CAPTCHA bots counter this with OCR engines, often trained using machine learning. They analyze pixel patterns and reconstruct letters with high accuracy. Even some moderately obfuscated CAPTCHA styles can now be cracked within milliseconds using open-source OCR libraries.
2. Image Recognition and AI Models
Modern bots are trained on thousands of CAPTCHA examples using tools like convolutional neural networks (CNNs). These models can detect objects in image challenges (like “select all the bicycles”) or identify audio CAPTCHA keywords. Some even use reinforcement learning to improve accuracy over time.
3. Browser Emulation and Behavior Simulation
Using headless browsers, CAPTCHA bots simulate user behavior—mouse movement, scroll speed, keyboard input, and even time delays—to mimic human interaction. They can fool behavioral detection tools by mimicking these actions in a natural pattern.
4. CAPTCHA Token Reuse
In some cases, bots solve one CAPTCHA challenge and reuse the token multiple times—especially when targeting misconfigured implementations. This strategy significantly lowers the cost and complexity of breaking CAPTCHA systems.
5. Human CAPTCHA Solvers
To overcome sophisticated challenges, some CAPTCHA bots route the challenge to human solvers in real time. These "captcha farms" exist in lower-income regions where workers are paid to solve CAPTCHAs manually, often earning pennies per 1,000 tasks. These platforms allow bot developers to integrate human solvers via API, creating hybrid bots that are hard to detect.
Together, these tactics make CAPTCHA bots a formidable threat—especially when combined with credential-stuffing attacks, phishing, or automated fraud schemes.
Risks and Consequences of CAPTCHA Bot Attacks
CAPTCHA bots are more than a technical curiosity—they’re a growing threat with serious real-world consequences. As automation becomes more accessible, businesses of all sizes must understand the risks:
1. Fake Accounts and Platform Abuse
Massive volumes of bot-generated accounts are used to flood online communities with spam, phishing links, or disinformation. These accounts may also skew marketing campaigns, loyalty programs, and referral systems—leading to financial losses and data pollution.
2. Account Takeovers (ATO)
Bots can be used to test millions of stolen username- password combinations in a practice called credential stuffing. Once an account is compromised, it can be used to steal personal data, make fraudulent purchases, or launch further attacks on the user’s contacts.
3. Pricing and Inventory Manipulation
CAPTCHA bots can monitor, extract, and react to dynamic pricing data faster than any human. They’re also used in scalping attacks, hoarding items like limited edition sneakers, GPUs, or concert tickets—often before real customers even get a chance.
4. Server Load and Infrastructure Costs
Malicious bots increase server load, consume bandwidth, and can even trigger rate-limiting or server crashes. This leads to increased hosting costs and degraded user experience, especially during high-traffic events.
5. Reputational and Legal Risks
Users expect platforms to be secure. A bot attack that exposes sensitive user data or enables fraud can result in reputational damage and potential fines under laws like GDPR or CCPA. Even if no data is stolen, simply allowing abuse to occur can erode user trust.
How to Protect Businesses from CAPTCHA Bots
CAPTCHA bots have rendered many traditional CAPTCHA methods less effective. However, due to their cost-efficiency and ease of use, CAPTCHAs remain a core part of online security. To stay protected, businesses must adopt a layered defense strategy.
1. Use CAPTCHA Alternatives
CAPTCHA alternative tools like honeypots, time-based checks, logic questions, device fingerprinting, and email/SMS verification can add extra layers of protection. While no single method is perfect, combining these with CAPTCHA helps balance security and user experience.
2. Upgrade to Advanced CAPTCHA Solutions
Advanced CAPTCHAs powered by AI and machine learning can detect bots through behavioral analysis, score-based assessments, and proof-of-work (PoW) systems.
GeeTest Adaptive CAPTCHA is a leading solution in this space. It offers adaptive security strategies, customizable challenges, and defenses that keep evolving with bot behavior. Backed by 12+ years of experience and trusted by over 360,000 businesses, it delivers reliable, scalable operation services for any online business.
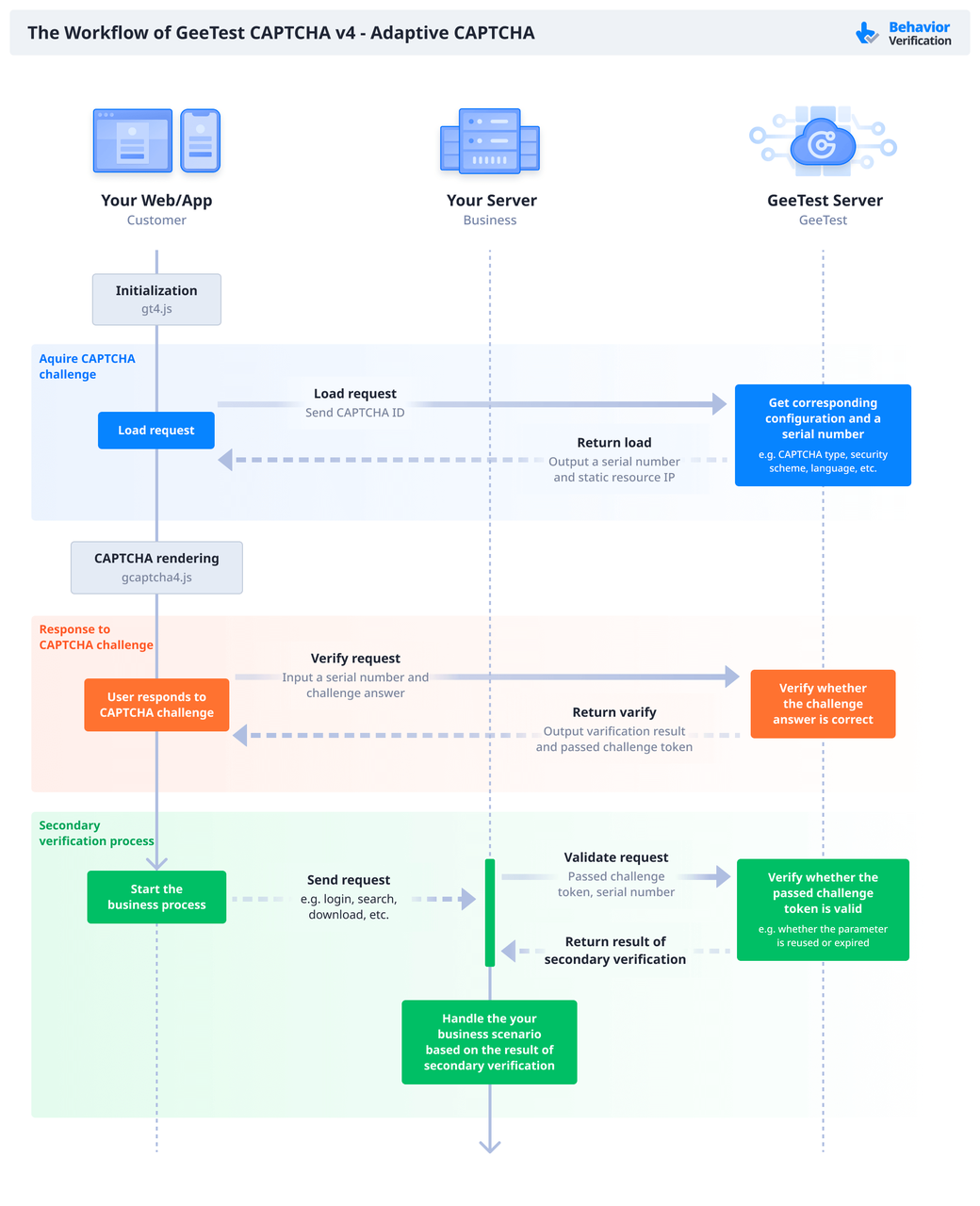
Final Thoughts
CAPTCHA bots are a growing threat that can overwhelm websites, steal data, and damage user trust. To fight back, businesses need adaptive tools that do more than just ask users to solve puzzles.
With GeeTest Adaptive CAPTCHA, you get a smarter, faster, and more secure way to stop bots before they cause harm.
Start protecting your digital assets today—get a free 30-day trial and see how GeeTest strengthens your defenses.
FAQ
Q1: What is a CAPTCHA bot?
A CAPTCHA bot is an automated program designed to bypass CAPTCHA tests that are meant to block non-human activity. These bots are often used in fraudulent activities like fake account creation, credential stuffing, data scraping, and inventory hoarding.
Q2: How do CAPTCHA bots work?
CAPTCHA bots use techniques such as OCR (optical character recognition), AI-based image recognition, behavioral emulation via headless browsers, and even human-in-the-loop solving farms to trick CAPTCHA systems. Advanced bots can also reuse solved tokens or integrate with CAPTCHA-solving APIs.
Q3: Why are CAPTCHA bots a threat to businesses?
They can cause financial loss, damage brand reputation, overload servers, and compromise user data. Businesses may also face legal consequences under data protection laws if bot activity leads to data exposure or system abuse.
Q4: Are traditional CAPTCHAs still effective?
Basic CAPTCHA types (e.g., distorted text) are increasingly ineffective against today’s sophisticated bots. While still useful in some cases, they should be combined with more advanced verification tools and behavioral analytics for better protection.
Q5: What are some alternatives to CAPTCHA?
Options include honeypots, time-based submission checks, simple math or logic challenges, device fingerprinting, and phone/email verification. These alternatives can supplement or replace traditional CAPTCHA systems in specific contexts.
Q6: What is an advanced CAPTCHA solution?
Advanced CAPTCHAs, like GeeTest Adaptive CAPTCHA, use AI, machine learning, and real-time threat data to detect bot-like behavior. These systems go beyond static challenges by scoring user interactions and adapting difficulty based on risk levels.
Q7: Can CAPTCHA bots be completely stopped?
While no solution offers 100% protection, layered defenses—combining CAPTCHAs, behavior tracking, and threat intelligence—can significantly reduce bot impact. The goal is to make attacks too costly or inefficient for bot operators.
Q8: Is GeeTest Adaptive CAPTCHA suitable for all industries?
Yes. Its flexible, API-based architecture and customizable verification flows make it suitable for industries like e-commerce, finance, gaming, education, SaaS, and more. It protects websites, mobile apps, and APIs alike.
Q9: How can I start using GeeTest Adaptive CAPTCHA?
You can start a free 30-day trial with GeeTest to explore its full capabilities. Integration is simple, and the solution includes expert support and access to real-time risk updates.

GeeTest
GeeTest
Subscribe to our newsletter