History of CAPTCHA - The Origin Story
06 Nov 2019 • 10 min read
History of CAPTCHA - The Origin Story
06 Nov 2019 • 10 min read
Born to save humans from the bad bots on the internet, got maddening with evolving technology, then became a chore that we just couldn’t do without. This is the origin story of the world wide web’s most overlooked guardian, CAPTCHA.
Bots Take On The Fight
It all began in 1997 when the search engine AltaVista was being abused by the automated submission of URLs into its library. The free "add URL" feature was crucial for AltaVista since it broadened its search coverage. Yet, some users have abused this feature by automating the submission of large numbers of URLs in an effort to skew AltaVista's ranking algorithm.
To distinguish whether the submission is made by a genuine human user or an automated bot, the Chief Scientist of AltaVista, Andrei Broder, and his colleagues developed an automated filter system that randomly generated an image of printed text which machine vision (optical character recognition, OCR) systems could not read while humans could. The system was so successful that after it'd been deployed for over a year, it had reduced the number of spam URLs by 95%. This is the first known deployment of an automated system to tell a human from a machine.
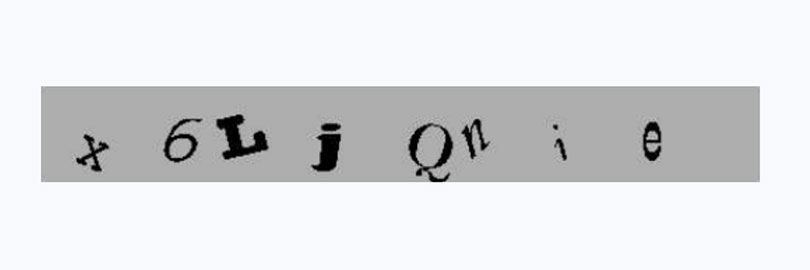
AltaVista CAPTCHA Word
Yahoo Bot Problem
Bot threats were not only a problem for AltaVista. In September of 2000, Udi Manber of Yahoo described this “chat room problem” to researchers at Carnegie Mellon University. Bots were joining online chat rooms to spam advertisements, which damaged the ecosystem considerably.
How Bots Could Be Denied Access?
Luis von Ahn and his colleagues have developed the GIMPY CAPTCHA, which picked random English words and rendered them as images of printed text under a wide variety of shape deformations and image occlusions. The user was asked to transcribe a number of words correctly. A simplified version called EZ-GIMPY, using only a single-word image was installed by Yahoo and was used in their chat rooms to restrict access to human users only.

Term "CAPTCHA" Born
Although both AltaVista Team and Carnegie Mellon Researchers have claimed to be the first to invent the CAPTCHA, the term was coined in 2003 by Luis von Ahn and his colleagues.
What does CAPTCHA Really Mean?
Turing test is a method of inquiry in artificial intelligence where a computer has to convince a human that it's a human. A reverse Turing test on the other hand is a human convincing a computer that it is not a computer. If you write a program that generates such a test automatically on the internet, then you got yourself the CAPTCHA: Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart.

The Evolution of CAPTCHA
CAPTCHA systems have been crucial in the ongoing battle against bots on the internet, but as these systems have evolved, they’ve faced an increasingly sophisticated array of challenges. From simple text-based tests to more complex behavioral analyses, the evolution of CAPTCHA reflects the rapid advancements in both bot technology and user experience demands. The original CAPTCHA was a simple, text-based test, but as bots became more capable, CAPTCHA technology had to adapt to stay ahead in the arms race between malicious bots and web security.
From Text to Images: The Rise of Image-based CAPTCHA
In the mid-2000s, as bots improved their recognition algorithms, text-based CAPTCHA systems became less effective. CAPTCHA systems started to evolve with the introduction of image-based challenges, requiring users to identify objects in distorted or partially occluded images. For example, users would be asked to "select all images with traffic lights" or "click on all images that contain buses." The introduction of these visual challenges represented a leap forward, as bots at the time had difficulty interpreting complex images, while humans could recognize even distorted objects with ease.
Despite this innovation, the arms race continued as AI models and machine learning algorithms improved, making it easier for bots to solve these image-based CAPTCHAs. CAPTCHA technology had to evolve further to keep pace with these developments.
Invisible CAPTCHA: Minimizing User Effort
As the user experience became an increasing focus of web developers, the next significant advancement in CAPTCHA technology came with the advent of Invisible CAPTCHA, pioneered by Google’s reCAPTCHA v2 and later v3. This system reduced user friction by eliminating the need for users to solve explicit CAPTCHA challenges, instead relying on behavioral data such as mouse movements and clicks to determine whether the user is a human or a bot. The now-famous "I’m not a robot" checkbox is a hallmark of this system, allowing users to verify themselves with a single click.
Invisible CAPTCHA systems, particularly reCAPTCHA v3, go even further by analyzing the user's interactions across the entire website, scoring the likelihood that they are a bot based on their behavior. This system operates seamlessly in the background, offering a frictionless experience for genuine users while preventing bots from gaining access to the site. However, as the technology advanced, new questions about privacy and user data began to emerge.
Behavioral and AI-Driven CAPTCHAs: Meeting the Bot Challenge
With bots continuing to grow more advanced, some CAPTCHA solutions have started to adopt even more sophisticated AI-driven methods. One notable example is GeeTest CAPTCHA, an advanced CAPTCHA solution that stands out for its ability to integrate behavioral analysis and machine learning to distinguish between humans and bots.
GeeTest CAPTCHA employs a dynamic sliding puzzle—a simple, intuitive user action in which the user is asked to slide a puzzle piece into place. This action, combined with machine learning algorithms that track user behavior, provides a highly effective way of detecting bots. Unlike traditional CAPTCHA systems that rely on static image recognition or text interpretation, GeeTest CAPTCHA evaluates users’ interactions, such as the speed and smoothness of their actions, to identify patterns that are difficult for bots to replicate.
GeeTest CAPTCHA: Redefining the CAPTCHA Experience

As bots became increasingly sophisticated, traditional CAPTCHA systems found it difficult to keep up with the speed and capabilities of modern bots. GeeTest CAPTCHA addresses this issue by leveraging behavioral biometrics and advanced machine learning to create a CAPTCHA system that is more difficult for bots to bypass while simultaneously being user-friendly.
GeeTest CAPTCHA eliminates many of the frustrating aspects of traditional CAPTCHA, such as having to identify distorted characters or select images from a grid. Instead, it focuses on a simple yet effective sliding puzzle challenge. This method not only offers a much smoother user experience but also strengthens security by analyzing user behavior. GeeTest's real-time behavioral analysis detects suspicious patterns or abnormalities in the user's interactions, which might indicate bot-like behavior, making it a far more secure alternative than older methods.
Beyond just improving security, GeeTest CAPTCHA also addresses the accessibility challenge, ensuring that users with disabilities, particularly those with visual or motor impairments, are not left behind. Its intuitive design is straightforward enough for users to navigate without frustration, while still providing the same high level of security.
A New Era of CAPTCHA: Security, Usability, and Accessibility
As AI-driven bots continue to evolve, CAPTCHA systems like GeeTest are becoming essential tools for balancing security, usability, and accessibility. The next generation of CAPTCHA solutions will likely focus even more on seamless, behavior-based methods that don’t require the user to solve explicit challenges. These systems will offer more secure, frictionless verification while minimizing the impact on user experience.
With the growing focus on privacy and user-centered design, the evolution of CAPTCHA technology will continue to prioritize machine learning, AI-powered behavioral analysis, and biometrics to provide robust security without creating unnecessary barriers for legitimate users. In the future, CAPTCHA will likely become even more integrated into the broader landscape of website security, leveraging deeper insights into user behavior while maintaining a balance with privacy concerns.
Conclusion: The Continuous Battle
CAPTCHA saved us from the bot threats at the time, what we didn’t know, however, was that this was just the beginning of the war of machine against machines where evolving bad bots and CAPTCHAs took it to the next level. Find out more on CAPTCHA Evolution | All Four Generations Explained.
The evolution of CAPTCHA showcases this continuous struggle between cyber attackers and web security developers. As bots grow more intelligent and capable, CAPTCHA systems must evolve to stay one step ahead, offering stronger protection while maintaining a seamless experience for legitimate users. Advanced solutions like GeeTest CAPTCHA represent the future of this technology: offering both enhanced security and a smooth, accessible user experience. Looking ahead, the demand for secure, user-friendly, and accessible verification methods will only increase, and CAPTCHA systems will continue to innovate to address these challenges.
Curious about the world’s leading enterprise-grade CAPTCHA solution? Try the demo or sign up for a free trial of GeeTest CAPTCHA to see how it can secure your website while enhancing user experience.
GeeTest
GeeTest
Subscribe to our newsletter