Understanding OTP Bot: How It Works and How to Stop It?
18 Apr 2025 • 10 min read
Understanding OTP Bot: How It Works and How to Stop It?
18 Apr 2025 • 10 min read
Is your business relying on two-factor authentication (2FA) such as one-time passwords (OTPs) to defend against the increasing sophistication of modern cybercriminals? OTPs and 2FA have long been hailed as silver bullets for stopping account takeovers (ATOs), but the reality is far more complex. With 52% of organizations now facing AI-enabled attacks on a daily or weekly basis, specialized OTP bots are actively exploiting flaws in these security measures. You’ve enabled 2FA on your accounts, and while you’re more secure than without it, fraudsters can still break in. This article dives into what OTP bots are, how they work, the threats they pose, and the best strategies to secure 2FA and stop these bots in their tracks—protecting both your business and your customers’ accounts from evolving tactics.
Understand OTPs (One-Time Passwords)
A One-Time Password (OTP) is a unique, temporary code used for authentication, providing an extra layer of security beyond traditional passwords. OTPs are typically sent via SMS, email, or generated through authentication apps like Google Authenticator or Authy. Unlike static passwords, OTPs are designed to be used once and expire within a short period, making it harder for cybercriminals to reuse stolen credentials.
Types of OTPs
- Time-Based OTPs (TOTP): Generated based on the current time and a secret key, usually through an authentication app. These OTPs change every few seconds.
- HMAC-Based OTPs (HOTP): Generated based on a counter instead of time, meaning they remain valid until used.
- SMS and Email OTPs: Sent via text message or email for user verification, commonly used by banks and online services.
OTPs play a critical role in industries such as banking (securing transactions), corporate systems (protecting VPN access), and e-commerce (reducing checkout fraud), offering advantages like compliance with standards (GDPR, HIPAA) and user-friendly integration. However, limitations persist, particularly with SMS-based delivery risks and device dependency. As a cornerstone of two-factor authentication (2FA), OTPs combine "something you know" (a password) with "something you have" (a device) to block most automated attacks, per Microsoft research. While OTPs significantly improve security, they are not infallible. Cybercriminals have developed various techniques, such as OTP bots, to intercept or trick users into revealing their authentication codes. Understanding these risks is crucial to staying protected.
What Are OTP Bots?
OTP bots are malicious automated tools designed to undermine the security of one-time passwords (OTPs) and bypass two-factor authentication (2FA). While OTPs add a critical layer of protection by requiring a temporary code—sent via SMS, email, or generated by apps like Google Authenticator—these bots exploit vulnerabilities in the delivery or human handling of these codes. Often sold as services on platforms like Telegram or dark web marketplaces, OTP bots empower cybercriminals, even those with limited technical skills, to target accounts at scale.
Their primary purpose? To trick users into revealing OTPs or intercept them directly, undermining the security that 2FA promises. With names like SMSRanger and BloodOTPbot popping up in underground markets, these tools have become a growing concern for individuals and businesses alike.
Types of OTP Bot
- SMS Interception Bots: These bots exploit weaknesses in telecom infrastructure, such as SS7 protocol vulnerabilities, to redirect or intercept SMS-based OTPs. Attackers use tools like SIM swap kits (purchased on the dark web) to hijack a victim’s phone number, allowing them to capture OTPs sent via text.
- Voice Phishing (Vishing) Bots: These bots use AI-driven voice calls or pre-recorded scripts to impersonate customer service agents from banks, tech companies, or government agencies. They trick victims into revealing OTPs by claiming their accounts have been compromised, creating urgency to make the victim act without thinking. Attackers often use regional accents and language variations to make the scam more convincing.
- SIM Swap Bots: Automate SIM swap fraud by submitting fake identity verification requests to telecom providers. Once the victim’s number is ported to an attacker-controlled SIM, all SMS OTPs are rerouted to the attacker.
- API Exploitation Bots: Target poorly secured authentication APIs to bypass OTP verification. For instance, if an API lacks rate-limiting, bots flood it with OTP guesses or intercept unencrypted OTP transmissions.
How OTP Bots Work?
OTP bots are powerful tools that cybercriminals use to bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA) by blending automation with social engineering. Some operate entirely on their own, while others trick victims into handing over critical information. Here’s how these bots compromise accounts in a few streamlined steps:
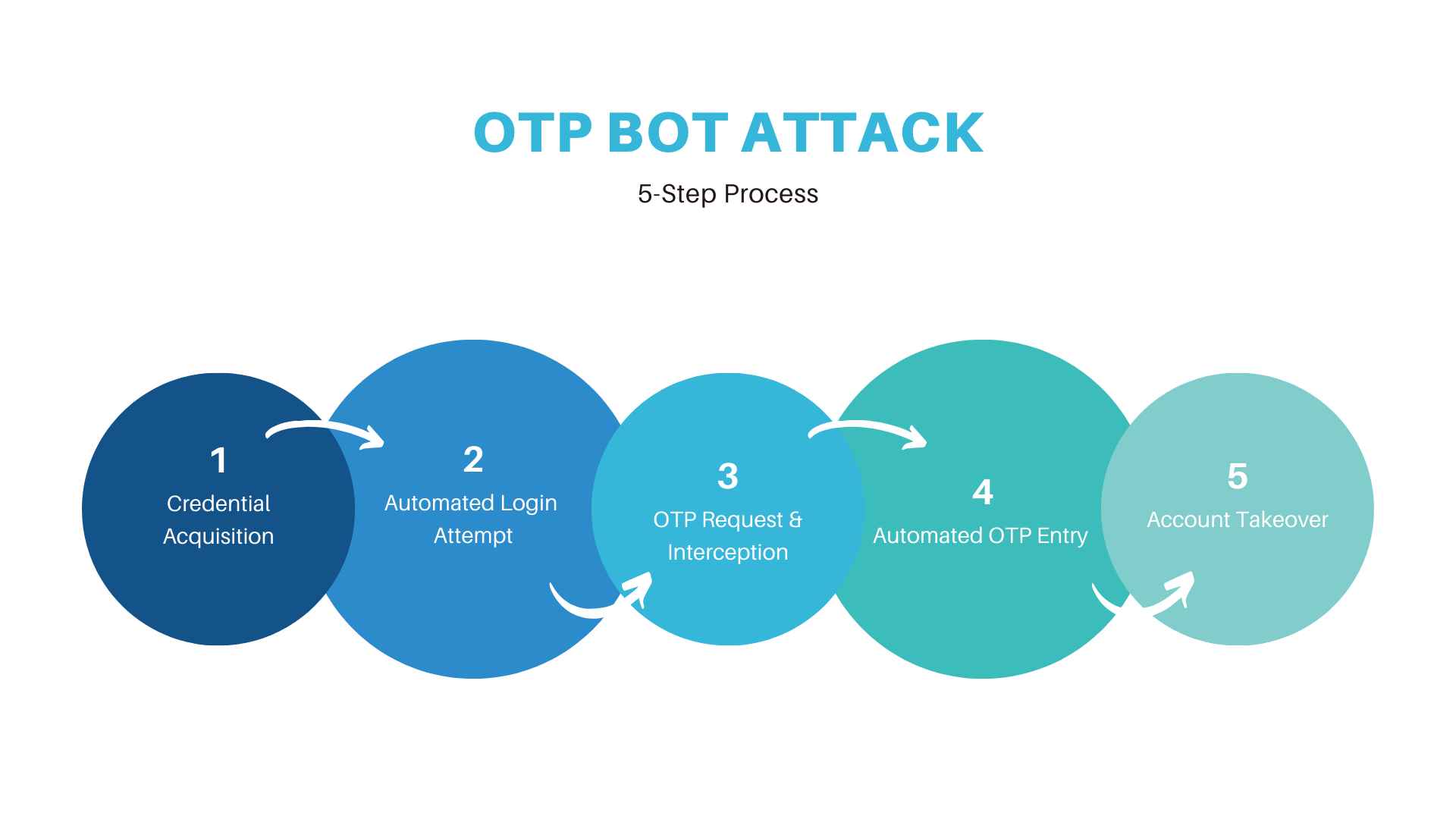
Step 1: Credential Acquisition
Before launching an OTP bot attack, cybercriminals first obtain the victim’s login credentials through methods such as:
- Phishing – Tricking users into entering their credentials on fake websites.
- Data Breaches – Using leaked usernames and passwords from security breaches.
- Credential Stuffing – Testing stolen credentials across multiple platforms, assuming users reuse passwords.
Step 2: Automated Login Attempt
Once the attacker has the credentials, they deploy an OTP bot to initiate a login attempt on the targeted website, app, or banking portal. Since these services often require an OTP for verification, the bot proceeds to trigger an OTP request.
Step 3: OTP Request & Interception Methods
When the login attempt is made, the system automatically sends an OTP to the victim’s registered phone number or email. OTP bots intercept these codes using one of the following techniques:
- SMS Interception – Some bots exploit vulnerabilities in the SS7 (Signaling System No. 7) protocol to reroute SMS messages to the attacker.
- Malware Attacks – Bots infect victims’ devices with malware that captures OTPs directly from their SMS inbox or authentication apps.
- Social Engineering (Vishing and Fake Calls) – More advanced OTP bots use AI-driven voice phishing (vishing) to impersonate customer support agents, claiming there is suspicious activity on the victim’s account and urging them to provide the OTP.
Step 4: Automated OTP Entry
Once the bot acquires the OTP, it rapidly enters the code and completes the login process seamlessly.on the target platform before the victim realizes the deception.
Step 5: Account Takeover
Once authenticated, the attacker gains full access, often altering passwords or contact details to lock out the victim. From there, they can execute fraudulent transactions or further exploit the account within seconds.
Risks of Malicious OTP Bots
The rise of OTP bots has led to several security threats, including:
- Financial Fraud: Attackers use OTP bots to bypass banking security measures and gain access to victims’ accounts, leading to unauthorized transactions.
- Identity Theft: Compromised OTPs enable hackers to take over personal accounts, leading to identity theft and data breaches.
- Corporate Data Breaches: Cybercriminals target employees in organizations to access sensitive corporate data using OTP bot attacks.
- Credential Stuffing Attacks: Hackers use stolen OTPs to automate login attempts on multiple platforms, increasing the risk of account takeovers.
How to Stop OTP Bots?
Detecting and stopping one-time password (OTP) bots requires a combination of proactive monitoring, advanced security measures, and user education. Here’s a breakdown of how to prevent them:
- Strengthen Authentication Methods: Move beyond SMS-based OTPs, which are vulnerable to interception. Use time-based OTPs (TOTP) via authenticator apps (e.g., Google Authenticator, Authy) or push notifications tied to a specific device. These are harder for bots to phish or intercept.
- Shorten OTP Validity: Reduce the expiration time of OTPs (e.g., 30 seconds instead of 5 minutes). This limits the window attackers have to use intercepted codes, making bot-driven attacks less effective.
- Rate Limiting: Restrict the number of OTP requests or login attempts allowed per user or IP within a set timeframe. This slows down bots and prevents them from overwhelming your system.
- Implement CAPTCHAs or Challenges: Add CAPTCHAs or JavaScript-based challenges to login flows. While advanced bots can sometimes bypass these, they still deter simpler scripts and increase the effort required for an attack.
- Bot Detection Tools: Deploy bot management solutions that use machine learning to identify and block automated traffic. These tools can analyze request patterns, headers, and behaviors to distinguish bots from humans.
- Educate Users: Warn users never to share OTPs, especially in response to unsolicited calls or messages claiming urgent account issues. Emphasize that legitimate services won’t ask for OTPs out of the blue.
- Adaptive Authentication: Use risk-based authentication that adjusts security based on context. For example, require additional verification (e.g., biometrics) for logins from new devices or high-risk locations.
- Block Suspicious IPs: Maintain an allowlist of trusted IPs and block or challenge requests from others. Combine this with geolocation checks to flag logins from unexpected regions.
Practical Steps for Implementation
- For Individuals: Regularly check account activity, use strong unique passwords, and opt for app-based 2FA over SMS. Report suspicious calls or messages to your service provider.
- For Businesses: Integrate bot detection into your security stack (e.g., via Web Application Firewalls or fraud prevention platforms). Leverage threat intelligence to stay ahead of emerging bot tactics and conduct regular security audits.
Mitigating OTP Bot Risks with GeeTest
GeeTest is an advanced CAPTCHA and bot management solution that helps protect authentication systems, like OTP verification flows, from automated abuse. Its unique approach—using behavioral biometrics and AI-powered risk analysis—makes it particularly effective against sophisticated OTP bots

Key Benefits of Using GeeTest for OTP Protection
Interactive CAPTCHA Challenges: GeeTest offers dynamic, gamified CAPTCHA challenges that are difficult for bots to solve but easy for real users. These can be added to:
- OTP request forms
- Login pages
- Account recovery workflows
Behavioral Detection: GeeTest analyzes user gestures like mouse movements, taps, and slide patterns. Bots often fail to replicate natural human behavior, making it easier to detect.
Adaptive Risk Control: Based on real-time analysis, GeeTest can dynamically increase challenge difficulty or block access completely for suspicious behavior, without compromising user experience.
Integration Flexibility: GeeTest supports multiple platforms (web, mobile apps, and APIs), making it ideal for businesses securing login flows, account creation, or OTP verification endpoints.
Prevent API Abuse: By integrating GeeTest before OTP generation endpoints, businesses can stop bots from abusing SMS gateways or brute-forcing OTP inputs.
Example Use Case
Before sending an OTP:
- Trigger a GeeTest CAPTCHA challenge.
- Only send the OTP if the user passes the challenge.
- Combine this with rate limiting and IP/device fingerprinting for an extra layer of defense.
Why GeeTest Over Traditional CAPTCHA?
Traditional CAPTCHAs are often beaten by modern bots using ML and OCR techniques. GeeTest, however, relies on interactive behavior analysis rather than static challenges, making it much more resilient.
Conclusion
Don’t let OTP bots compromise your security. The battle against OTP bots isn’t just about technology—it’s about building a culture of security. For businesses, this means integrating tools like GeeTest CAPTCHA into your authentication workflows, conducting regular audits, and staying updated on emerging bot tactics. For users, vigilance is key: monitor account activity and report suspicious requests immediately.
By combining AI-powered bot management, user education, and adaptive authentication, organizations can turn the tide against OTP fraud. Remember: no single solution is foolproof, but a layered defense significantly raises the cost for attackers. Protect your digital assets today by prioritizing innovation, collaboration, and proactive threat mitigation.
GeeTest
GeeTest
Subscribe to our newsletter
