Moz DotBot Web Crawler: What It Is and How It Works in 2025
25 Jul 2025 • 10 min read
Moz DotBot Web Crawler: What It Is and How It Works in 2025
25 Jul 2025 • 10 min read
Web crawlers play a fundamental role in how search engines and SEO tools discover, analyze, and index online content. These automated programs systematically browse websites to gather information that powers various digital services, including search rankings, backlink analysis, and domain authority scoring.
Among the well-known SEO-focused crawlers is Moz DotBot, developed by Moz, a leading SEO software provider. As of 2025, Moz DotBot continues to be an important crawler for site owners who want visibility and accurate metrics within Moz tools. This article offers an in-depth look at what Moz DotBot is, how it operates, and how website administrators can manage its access effectively.
What Is Moz DotBot?
Moz introduced DotBot to improve the accuracy and depth of its SEO data. Over the years, the crawler has evolved to keep up with changes in website technology and SEO needs. Early versions of DotBot focused on basic site indexing and link discovery. As SEO became more complex, Moz updated DotBot to analyze content quality, site structure, and link profiles more effectively. By 2025, DotBot uses advanced crawling techniques and machine learning models to gather data efficiently. The bot now adapts its crawling frequency based on site characteristics and user requests through Moz tools. Moz has also improved DotBot’s compliance with web standards, ensuring it respects robots.txt directives and minimizes server impact. The crawler’s evolution reflects Moz’s commitment to providing reliable SEO insights while maintaining ethical crawling behavior.
How Moz DotBot Differs from Other Web Crawlers?
![]()
How DotBot Crawls?
Machine Learning Model
DotBot uses a machine learning model to improve its crawling and indexing process. The model helps the bot decide which pages to visit and how often to return. DotBot learns from past crawling patterns and adapts to changes on websites. This approach allows the crawler to focus on high-value pages, such as those with fresh content or important links. By using machine learning, DotBot reduces unnecessary requests and avoids overloading servers. Many modern web crawlers now use similar technology, but DotBot’s model stands out for its focus on SEO data collection.
User-Agent Identification
Every time DotBot visits a website, it identifies itself with a unique user-agent string. Site owners can spot this string in their server logs. The user-agent string usually looks like this:
Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; DotBot/2.0; +https://dotbot.com/about/)
This identification helps webmasters recognize DotBot among other crawling bots. Search bots and SEO crawlers often use clear user-agent strings to show their purpose. DotBot’s transparency makes it easier for site owners to manage access and monitor activity.
Data Collected
DotBot gathers a wide range of data during its crawling process. The bot collects information about page titles, meta descriptions, headings, and internal links. It also records external links, images, and page structure. This data supports Moz’s SEO tools by helping users analyze backlink profiles and site health. DotBot does not collect personal information or sensitive data. Instead, the crawler focuses on technical SEO elements and link analysis. Other web crawlers may collect broader data, but DotBot targets information that improves SEO metrics and site audits.
Respect for Robots.txt
Most web crawlers follow the rules set in a website’s robots.txt file. This file tells crawling bots which pages they can visit and which ones to avoid. DotBot claims to respect robots.txt directives, but real-world reports show mixed results. Many server logs reveal that DotBot sometimes ignores these rules. Users have noticed DotBot making repeated requests to pages that robots.txt blocks. Community discussions often mention this behavior, raising concerns about the bot’s compliance. No formal research exists on this topic, but practical server logs and user feedback highlight the issue.
- Web server logs show DotBot sometimes ignores robots.txt directives.
- Multiple log entries record DotBot making requests to blocked pages.
- Community forums discuss DotBot’s inconsistent behavior.
- No academic studies confirm or deny these observations.
Note: Site owners should monitor DotBot’s activity and update their robots.txt files as needed. If problems continue, contacting Moz support may help resolve issues.
Why DotBot Visits Sites
Triggers for Crawling
DotBot visits websites for several reasons. The bot aims to collect fresh data for Moz’s SEO tools. When a website updates its content or structure, DotBot may schedule a new crawl. Moz users who request site audits or backlink checks can also trigger DotBot to visit specific pages. The bot uses signals like sitemap updates, new inbound links, or changes in robots.txt to decide when to crawl. DotBot’s machine learning model helps it prioritize which sites and pages to visit first. Unlike some crawling bots that scan the web randomly, DotBot focuses on gathering information that improves SEO analysis.
Benefits for Site Owners
Site owners gain several advantages when DotBot visits their sites. The bot helps Moz build a detailed link index, which supports accurate SEO metrics. These metrics include Domain Authority and Page Authority, which many marketers use to measure site strength. DotBot’s data collection allows site owners to discover new backlinks and spot technical issues. Moz’s tools use this information to provide actionable SEO recommendations. When DotBot crawls a site, it can reveal broken links, duplicate content, or missing metadata. This process helps site owners improve their search visibility and site health. DotBot does not collect sensitive or personal data, so privacy remains protected.
Challenges and Considerations of Moz DotBot Access
While Moz DotBot is designed to be efficient and non-intrusive, its crawling activities can present challenges, particularly for websites with specific technical or operational constraints. Understanding these challenges and implementing effective solutions is key to balancing DotBot’s SEO benefits with site performance.
1. High Bandwidth Usage
For large websites or those with frequent content updates, DotBot’s crawling can consume significant bandwidth. Sites with thousands of pages, dynamic content, or high-traffic profiles may experience increased data transfer demands, potentially affecting hosting costs or site performance during peak periods.
2. Server Load and Resource Strain
DotBot’s frequent or aggressive crawling can strain server resources, especially for sites hosted on shared or low-capacity servers. This is particularly problematic for sites with limited CPU, memory, or database resources, where simultaneous requests from DotBot and other crawlers (e.g., Googlebot) can lead to slowdowns or timeouts.
3. Crawl Overlap with Other Bots
DotBot often crawls alongside other web crawlers, such as those from Google, Bing, or third-party SEO tools. This overlap can exacerbate server load, particularly if multiple crawlers access resource-intensive pages like product listings or media-heavy sections simultaneously.
4. Indexing Sensitive or Low-Value Pages
Without proper configuration, DotBot may crawl and index pages that are irrelevant to SEO, such as internal admin pages, duplicate content, or temporary URLs. This can skew Moz’s Link Index data, leading to inaccurate SEO metrics or unnecessary server load.
5. Dynamic IP Challenges
DotBot uses dynamic IP addresses hosted on services like Wowrack, making it difficult to whitelist or blacklist based on IP alone. This can complicate bot management for sites relying on IP-based access controls.
How to Block Moz DotBot?
While Moz DotBot is a legitimate SEO crawler, there are scenarios where you might want to restrict its access to your website to conserve server resources or protect sensitive content. Here are several effective methods to block DotBot:
1. Restrict Access via robots.txt File
The simplest way to instruct DotBot not to crawl your site is by adding rules in your website’s robots.txt file, located in the root directory. To block DotBot entirely, include the following:
User-agent: dotbot
Disallow: /
This tells DotBot it is not allowed to access any pages on your site. Keep in mind that most well-behaved crawlers respect robots.txt, but some bots may ignore it.
2. Deny Access Using the .htaccess File (Apache Servers)
For a more robust and server-level block, you can configure your .htaccess file to reject requests from DotBot by detecting its user-agent string. Add this code to your .htaccess:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP_USER_AGENT} dotbot [NC]
RewriteRule .* - [F,L]
This setup causes the server to respond with a 403 Forbidden status to any DotBot requests, effectively blocking access.
3. Block Specific IP Addresses
If you know the IP ranges used by DotBot, you can block those IPs directly via your server firewall or in your .htaccess file. For example:
order allow,deny
deny from 123.456.789.0
allow from all
Replace 123.456.789.0 with the actual DotBot IP address or IP range. This method requires you to maintain and update the list of IPs regularly for continued effectiveness.
4. Use CAPTCHA Solutions to Prevent Automated Access
While blocking Moz DotBot may serve specific goals such as reducing crawl frequency or excluding your site from Moz’s index. But DotBot is just one of thousands of bots that visit websites daily. Many of these bots are not as well-behaved. Some scrape content, attempt credential stuffing, or overload site infrastructure. Therefore, a comprehensive bot management strategy is essential.
CAPTCHAs are effective in distinguishing between human users and automated bots. Implementing CAPTCHA challenges on pages like login forms, search, or comment sections can reduce unwanted bot traffic.
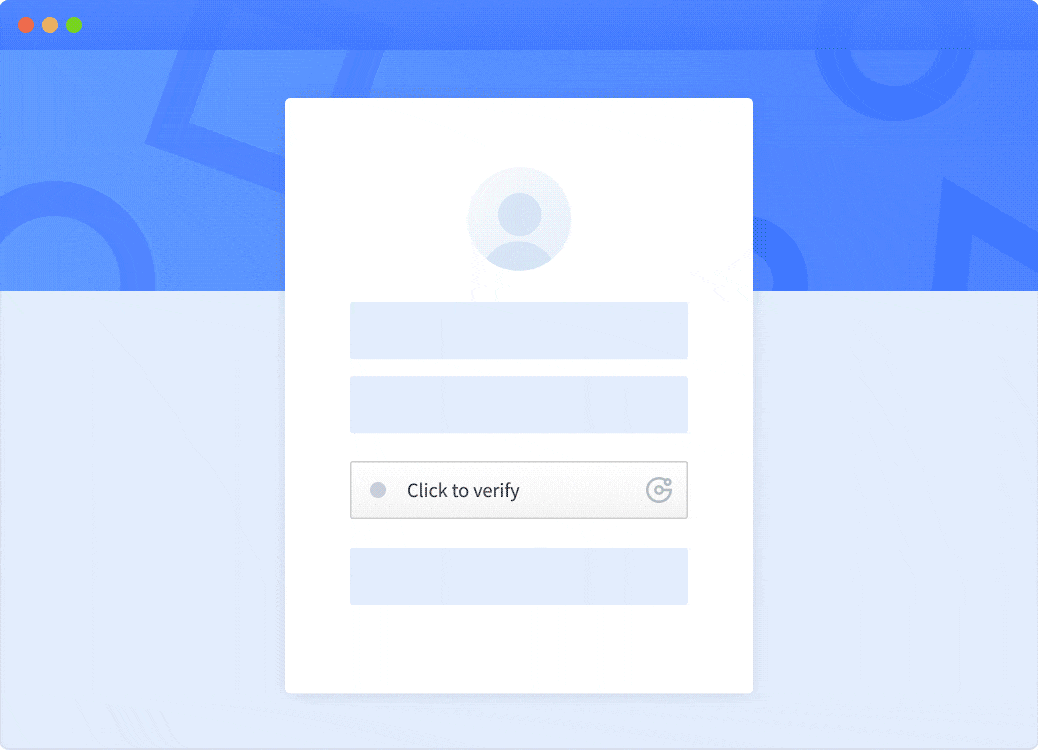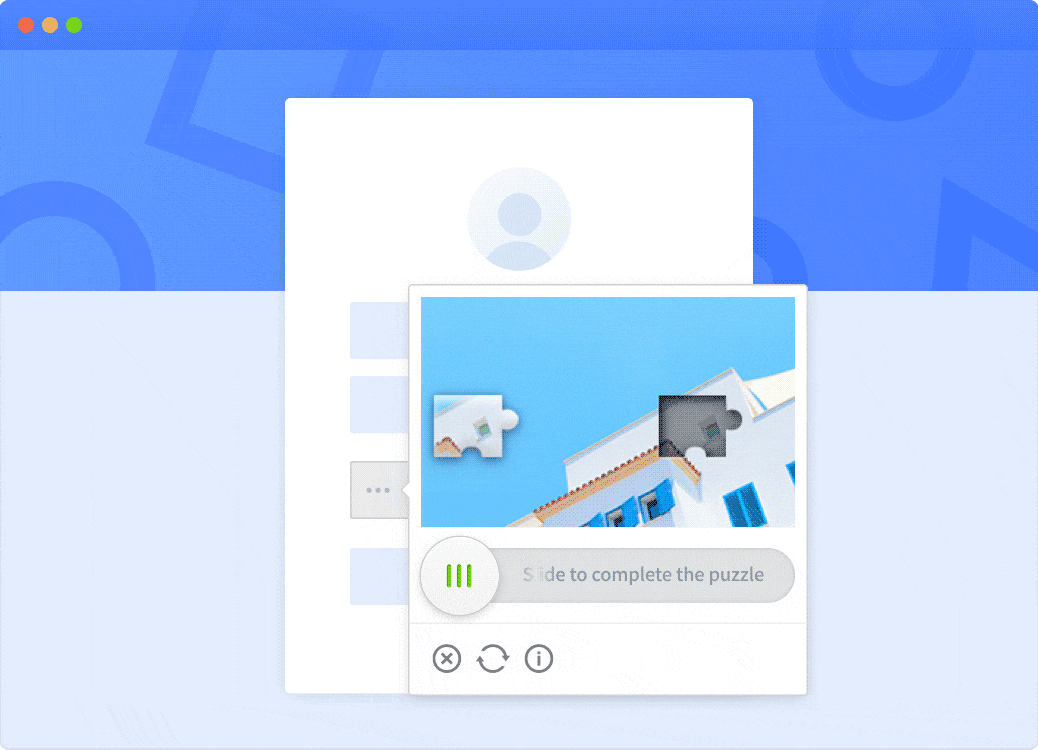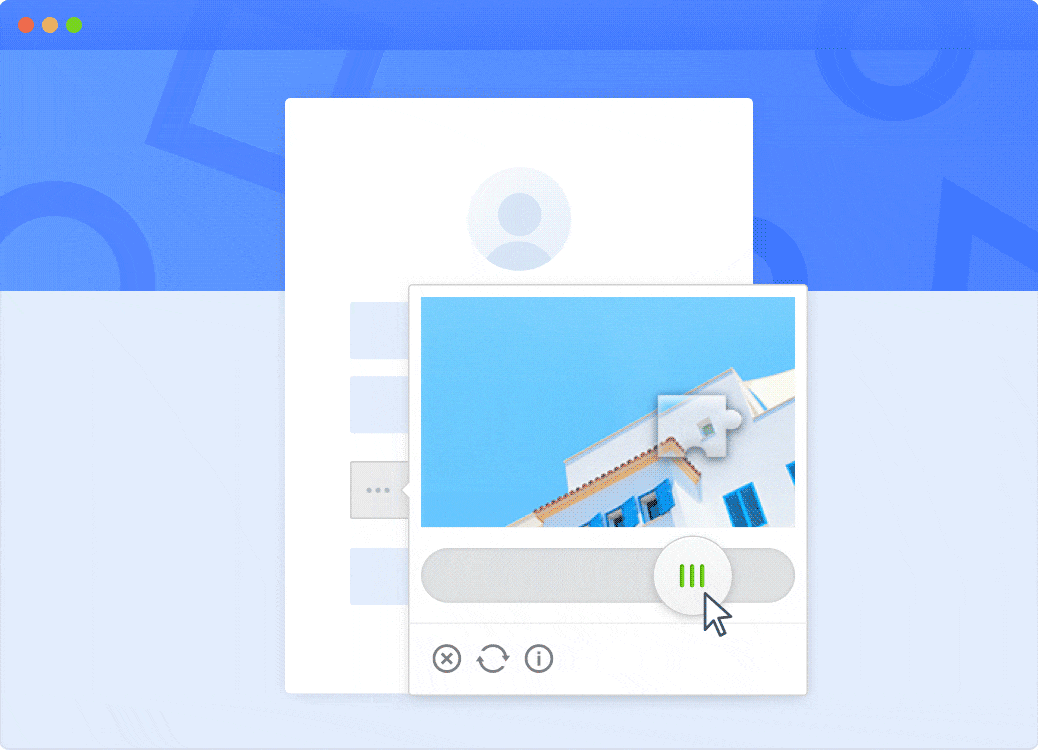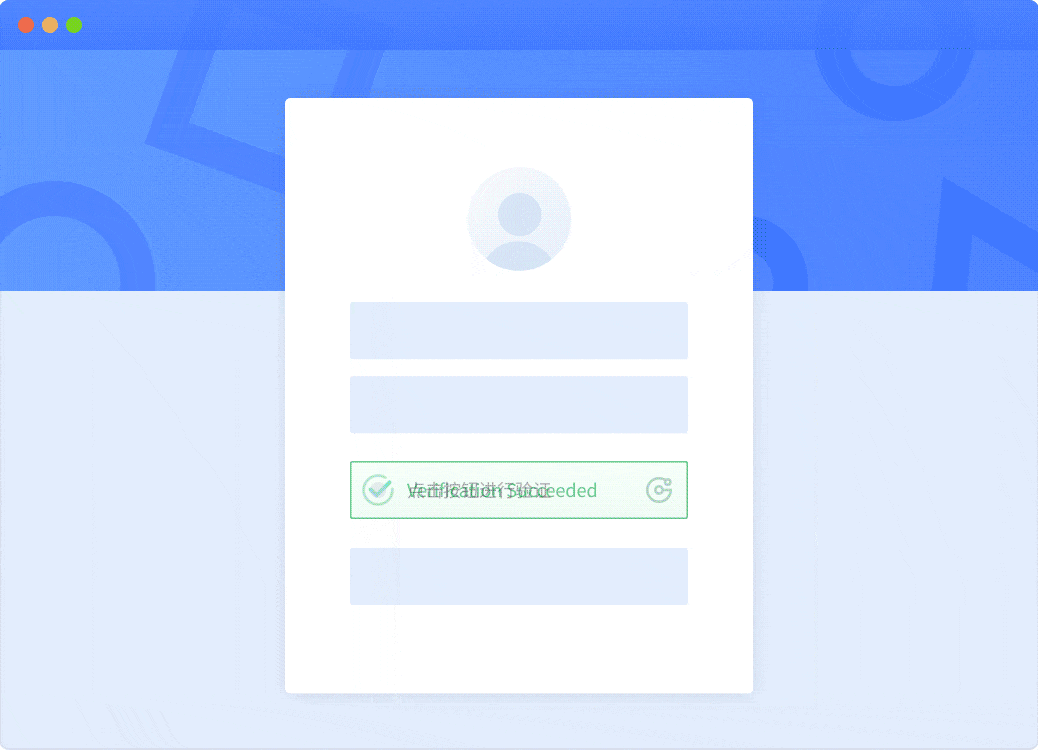
GeeTest CAPTCHA Helps Block Unwanted Bots
GeeTest CAPTCHA goes beyond traditional image or checkbox CAPTCHAs by leveraging behavioral biometrics and real-time risk analysis to identify automated access attempts before they impact your site.
Key Features of GeeTest CAPTCHA for Bot Prevention:
- Behavior-Based Bot Detection: GeeTest analyzes a user’s interaction patterns—mouse movement, click dynamics, and drag speed to detect non-human behavior with high accuracy.
- Adaptive CAPTCHA Challenges: Based on risk level, GeeTest dynamically serves sliding puzzles, click challenges, or invisible verifications to optimize both security and user experience.
- Invisible Verification Mode: Low-risk users can pass verification without ever seeing a challenge, while suspicious traffic receives a stronger barrier, ensuring friction only where needed.
- Device and Session Fingerprinting: Identifies botnets, proxy users, and headless browsers via advanced fingerprinting, enhancing protection against scraping, spam, and brute-force attempts.
- Flexible Integration: Supports websites, mobile apps, and third-party systems via lightweight SDKs and APIs. Integrates easily with CMS platforms, login systems, and ecommerce flows.
- Custom Whitelisting/Blacklisting Rules: You can configure GeeTest to challenge unknown bots while allowing access to trusted crawlers like Moz DotBot, Googlebot, or Bingbot, preserving your SEO data flow.
Conclusion
Moz DotBot remains a valuable SEO crawler in 2025, offering essential insights into backlinks, domain authority, and site structure. However, like many automated bots, its crawling activity can pose challenges, ranging from bandwidth strain to indexing of non-essential pages. A balanced approach is key: allow DotBot when it aligns with your SEO goals, but deploy intelligent controls to protect your site’s performance and data.
For site owners looking to strengthen their bot management strategy, GeeTest CAPTCHA offers a modern, AI-powered solution that goes beyond basic verification. Its behavioral analysis and adaptive challenges help block malicious bots while maintaining a smooth user experience.
Take control of your site’s security and traffic quality—try GeeTest CAPTCHA Demo and experience the difference.
.png)
GeeTest
GeeTest
Subscribe to our newsletter