Protecting Against Credential Stuffing: Lessons from the Paypal Breach
29 Mar 2023 • 10 min read
Protecting Against Credential Stuffing: Lessons from the Paypal Breach
29 Mar 2023 • 10 min read
Cyberattacks have become increasingly common and sophisticated, and one such attack that has gained popularity is credential stuffing. According to Credential Stuffing 2022: The latest trends and tools, a report issued by F5, credential stuffing is the top enterprise attack, and over 80% of hacking-related breaches involve brute force or the use of lost or stolen credentials. Furthermore, over 15 billion stolen credentials are currently circulating on the dark web, according to Digital Shadows, providing a wealth of information for cybercriminals to use. Okta, a cloud-based identity, and access management provider, also released a report stating that credential stuffing accounts for 34% of all login attempts across all industries.
In this article, we'll discuss what credential stuffing is, why it's a growing threat, and how you can protect your business from becoming a victim.
PayPal Suffers Large-Scale Credential Stuffing Attack
In early 2023, Paypal reported a significant credential stuffing attack that impacted around 35,000 of its users. Cybercriminals used proxies and automated tools to repeatedly try login credentials obtained from other breaches on Paypal's login page. A breach notification indicates that the credential stuffing attack took place from December 6 to December 8, 2022, when PayPal detected the attack and cut off login attempts. On December 20, however, the company verified that a small number of PayPal accounts had been successfully accessed by the attackers. While no unauthorized transactions were detected, the incident underscores the risk posed by credential stuffing attacks. PayPal has since renewed calls for multi-factor authentication and urged users to regularly update their passwords to protect their personal information. Though this data incident was resolved, it is crucial to note that the stolen logins may still pose a threat as they could potentially be reused across multiple accounts. This event serves as a wake-up call for individuals and businesses to implement enhanced security controls to mitigate the risk of credential stuffing attacks.
What is Credential Stuffing?
Credential stuffing is a type of cyberattack in which hackers use automated scripts to try compromised credentials, which are usually username and password pairs, on multiple websites, hoping to gain access to at least one. These scripts can try thousands or even millions of combinations in a short amount of time. Once attackers find a match, they will quickly take over the user's account (ATO) and perform fraudulent activities, such as making unauthorized purchases.
How Do Credential Stuffing Attacks Work?
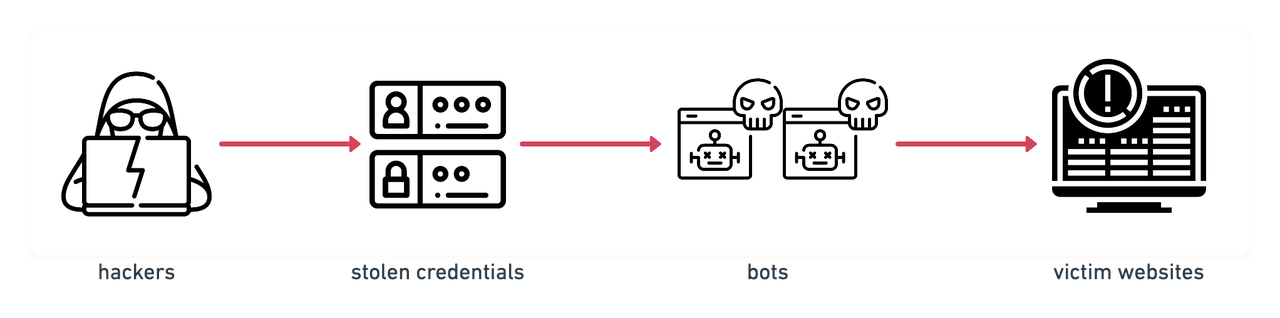
credential stuffing attacks workflow
A typical scenario of Credential Stuffing Attacks is that the hackers set up some sophisticated bots that can automatically execute the process of attempting several logins with stolen login credentials across multiple websites in parallel while forging different IP addresses. So credential stuffing attacks would appear on the target website just like regular network traffic; otherwise, suspicious high-volume traffic from a single IP address would raise the site's suspicion, and the hackers might get intercepted.
Once they find a site where a set of stolen credentials work, they will have access to the user's personally identifiable information(PII) and other valuable data from compromised accounts, which will be prepared for fraudulent activities that will be coming next.
What's the Difference Between Credential Stuffing and Other Attacks?
Brute Force Attacks, also known as Brute Force Cracking, in which the attacker uses trial-and-error to guess passwords without any clues and take multiple attempts with all possible password combinations. Credential Stuffing is similar to Brute Force Attack, however, it uses proven legitimate credentials(usually obtained through data breaches at other organizations), illegally though, which will greatly reduce the number of login attempts on one account in a short period of time.
Brute force attacks can be defended by a strong password consisting of characters, numbers, and uppercase letters. However, password strength does not have much effect on credential stuffing attacks. As long as a credential is shared on multiple platforms, no matter how strong the password is, credential stuffing will threaten them if there is a compromised one.
Besides, Credential Cracking, Token Cracking, and Card Cracking are categorized as subsets of Brute Force Attacks by OWASP.
Why Are Credential Stuffing Attacks Possible?
Password-based authentication is a common identity mechanism for access to online platforms. However, password reuse is also a common practice. In 2019, Google's research showed that 52% of users reuse passwords for multiple websites, which might cause users potential losses on other platforms if accounts on one server are compromised. This figure is growing year by year, and according to the Auth0 State of Secure Identity 2022 report, 87% of users reuse passwords across multiple accounts, making it easier for cybercriminals to use stolen credentials to access other accounts.
Moreover, the rise of automated bots and tools for credential stuffing has made it easier for cybercriminals to launch these attacks at scale. User credentials are not safe since passwords are prone to phishing attacks, malware/ransomware attacks, keyloggers, and sniffers that weaken their effectiveness. Additionally, the trading of stolen credentials on secret networks is a thriving business. In 2020, the Digital Shadows Photon Research team revealed that the number of stolen usernames and password pairs was 15 billion-plus across the dark web, and the average cost of a single account was $15.43, making credential stuffing attacks a low-entry-cost activity.
How to Prevent and Mitigate Credential Stuffing Attacks?
Suggest a Unique Password for Each Account
Password reuse is the primary cause of credential stuffing attacks. To prevent these types of attacks, enforcing strong password policies and encouraging users to create unique and complex passwords for each account is crucial. Disallowing email addresses as User IDs is also recommended. While it's not possible to force everyone to do this, one effective way to handle this challenge is to use password managers to generate unique and complex passwords for each account. These passwords can then be encrypted and stored in a secure password vault. Besides, individuals and businesses better regularly check their accounts for any suspicious activity, such as unauthorized logins or transactions, and report any incidents to the account provider immediately.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication(MFA) is an effective mitigation strategy to protect against credential stuffing attacks because it requires users to provide two or more forms of authentication in addition to username and password combinations. For instance, users can be asked to complete a CAPTCHA test, provide a fingerprint, or enter a temporary code sent to a secured account. These additional factors or steps provide other obstacles to deter attackers. In practice, automated phishing and account takeover (ATO) tools may bypass MFA, but it remains a more challenging method to implement than credential stuffing attacks.
Use Device Fingerprinting
A device fingerprint can be created by combining various attributes (hardware and software information) such as operating system, browser, language, installed fonts, screen resolution, etc. This fingerprint can typically be used to protect against suspicious attempts on multiple accounts that might indicate a potential credential stuffing attack.
Create IP Blacklisting
IP Blacklisting is a strategy that is often used to filter out illegitimate and malicious IP addresses that attempt to access your network. Attackers frequently attempt to execute credential stuffing using a limited range of IP addresses. Adding them to a blacklist is another effective way to defend against multiple attempts originating from these suspicious IP addresses. The caveat here is that this method may result in some false positives if not closely monitored and compared.
Final Thoughts
The recent Paypal incident serves as a stark reminder of the prevalence and potential impact of credential stuffing attacks. The repercussions of such attacks can extend far beyond the initial breach and can affect multiple accounts where the same login credentials are being reused. As individuals and businesses, it is imperative to take proactive measures to enhance security controls and mitigate the risk of such attacks. This includes avoiding password reuse, implementing multi-factor authentication, using IP blacklisting, and employing device fingerprinting techniques.
Furthermore, adopting GeeTest's advanced bot detection and mitigation solutions can enable businesses to accurately detect and cut off risk signals in real time, preventing credential stuffing attacks from causing widespread damage. By prioritizing security measures and staying vigilant, we can safeguard ourselves and our businesses against the growing threat of credential stuffing attacks.
Selvia Zheng
Marketing Specialist @ GeeTest
Subscribe to our newsletter
